# Table of Contents
# 자료 구조의 종류
자료 구조는 크게 선형 구조와 비선형 구조로 나뉜다.
- 선형 구조
ArrayDynamic Array (ArrayList)LinkedListStackQueueDeque
- 비선형 구조
TreeGraph
# Array
배열(Array)는 다음과 같은 특징이 있다.
- 배열이 생성될 때 크기가 고정되며, 크기를 변경할 수 없다.
- 데이터 읽기, 쓰기, 변경은
Random Access가 가능하므로O(1)의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다. - 물리적으로도 메모리 상에서 근접하게 위치하는
지역성을 갖는다.
1차원 배열은 다음과 같이 선언한다.
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
2차원 배열은 다음과 같이 선언한다.
int[][] numbers = {
{ 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 }
};
# Dynamic Array
Dynamic Array는 다음과 같은 특징이 있다.
- 배열의 크기를 변경할 수 있다.
- 일반적으로
Array크기가 꽉 차면, 두 배 크기의 새로운Array를 생성한 후 데이터를 복사한다.
Java에서는 ArrayList가 Dynamic Array의 역할을 한다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
ArrayList<Integer> dArr = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 데이터 추가
dArr.add(1);
dArr.add(2);
dArr.add(3);
// 데이터 변경
dArr.set(1, 5);
// 데이터 접근
dArr.get(1);
// 데이터 삭제
dArr.remove(2);
# LinkedList
LinkedList는 내부적으로 Array 대신 다음 노드의 주소값을 저장하는 노드(Node)를 사용한다.
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedList<T> {
class Node<T> {
private T data;
public Node next;
}
// ...
}
Java에서는 다음과 같이 LinkedList를 사용할 수 있다.
List<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<Integer>();
// 데이터 추가
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.add(3);
# Stack
Stack은 FILO(First-in, Last-out)의 자료구조다.
import java.util.Stack;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.pop(); // 2
stack.pop(); // 1
# Queue
Queue는 FIFO(First-in, Last-out)의 자료구조다. Queue인터페이스와 LinkedList클래스로 구현할 수 있다.
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.peek(); // 1
queue.remove(); // 1
queue.remove(); // 2
# 기능 개발
기능 개발
프로그래머스 팀에서는 기능 개선 작업을 수행 중입니다. 각 기능은 진도가 100%일 때 서비스에 반영할 수 있습니다.
또, 각 기능의 개발속도는 모두 다르기 때문에 뒤에 있는 기능이 앞에 있는 기능보다 먼저 개발될 수 있고, 이때 뒤에 있는 기능은 앞에 있는 기능이 배포될 때 함께 배포됩니다.
먼저 배포되어야 하는 순서대로 작업의 진도가 적힌 정수 배열 progresses와 각 작업의 개발 속도가 적힌 정수 배열 speeds가 주어질 때 각 배포마다 몇 개의 기능이 배포되는지를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성하세요.
- 제한 사항
- 작업의 개수(progresses, speeds배열의 길이)는 100개 이하입니다.
- 작업 진도는 100 미만의 자연수입니다.
- 작업 속도는 100 이하의 자연수입니다.
- 배포는 하루에 한 번만 할 수 있으며, 하루의 끝에 이루어진다고 가정합니다. 예를 들어 진도율이 95%인 작업의 개발 속도가 하루에 4%라면 배포는 2일 뒤에 이루어집니다.
# 주식 가격
주식 가격
- 문제설명
초 단위로 기록된 주식가격이 담긴 배열 prices가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 가격이 떨어지지 않은 기간은 몇 초인지를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성하세요.
- 제한사항
prices의 각 가격은 1 이상 10,000 이하인 자연수입니다. prices의 길이는 2 이상 100,000 이하입니다.
- 입출력 예
| prices | prices |
|---|---|
| [1, 2, 3, 2, 3] | [4, 3, 1, 1, 0] |
- 입출력 예 설명
- 1초 시점의 ₩1은 끝까지 가격이 떨어지지 않았습니다.
- 2초 시점의 ₩2은 끝까지 가격이 떨어지지 않았습니다.
- 3초 시점의 ₩3은 1초뒤에 가격이 떨어집니다. 따라서 1초간 가격이 떨어지지 않은 것으로 봅니다.
- 4초 시점의 ₩2은 1초간 가격이 떨어지지 않았습니다.
- 5초 시점의 ₩3은 0초간 가격이 떨어지지 않았습니다.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] prices) {
ArrayList<Integer> answerList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> queue = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i=0; i<prices.length; i++) {
for (int j=i+1; j<prices.length; j++) {
if (prices[i] <= prices[j]) {
queue.add(prices[j]);
// System.out.println(queue.toString());
}
else {
// System.out.println("prices[i] > prices[j]");
queue.add(prices[j]);
break;
}
}
answerList.add(queue.size());
queue.clear();
}
// System.out.println(answerList.toString());
int[] answer = new int[answerList.size()];
for (int i=0; i<answerList.size(); i++) answer[i] = answerList.get(i);
return answer;
}
}
# 다리를 지나는 트럭
다리를 지나는 트럭
- 문제 설명
트럭 여러 대가 강을 가로지르는 일차선 다리를 정해진 순으로 건너려 합니다. 모든 트럭이 다리를 건너려면 최소 몇 초가 걸리는지 알아내야 합니다. 다리에는 트럭이 최대 bridge_length대 올라갈 수 있으며, 다리는 weight 이하까지의 무게를 견딜 수 있습니다. 단, 다리에 완전히 오르지 않은 트럭의 무게는 무시합니다.
예를 들어, 트럭 2대가 올라갈 수 있고 무게를 10kg까지 견디는 다리가 있습니다. 무게가 [7, 4, 5, 6]kg인 트럭이 순서대로 최단 시간 안에 다리를 건너려면 다음과 같이 건너야 합니다.
| 경과 시간 | 다리를 지난 트럭 | 다리를 건너는 트럭 | 대기 트럭 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | [] | [] | [7,4,5,6] |
| 1~2 | [] | [7] | [4,5,6] |
| 3 | [7] | [4] | [5,6] |
| 4 | [7] | [4,5] | [6] |
| 5 | [7,4] | [5] | [6] |
| 6~7 | [7,4,5] | [6] | [] |
| 8 | [7,4,5,6] | [] | [] |
따라서, 모든 트럭이 다리를 지나려면 최소 8초가 걸립니다.
solution 함수의 매개변수로 다리에 올라갈 수 있는 트럭 수 bridge_length, 다리가 견딜 수 있는 무게 weight, 트럭 별 무게 truck_weights가 주어집니다. 이때 모든 트럭이 다리를 건너려면 최소 몇 초가 걸리는지 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성하세요.
제한 조건
- bridge_length는 1 이상 10,000 이하입니다.
- weight는 1 이상 10,000 이하입니다.
- truck_weights의 길이는 1 이상 10,000 이하입니다.
- 모든 트럭의 무게는 1 이상 weight 이하입니다.
입출력 예
| bridge_length | weight | truck_weights | return |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 10 | [7,4,5,6] | 8 |
| 100 | 100 | [10] | 101 |
| 100 | 100 | [10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10] | 110 |
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int bridgeLength, int bridgeLimit, int[] truckWeights) {
int time = 0;
int sum = 0;
ArrayList<Integer> queue = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int truckWeight: truckWeights) {
while(true) {
// Queue가 비어있다면
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
queue.add(truckWeight);
sum = sum + truckWeight;
time ++;
break;
// Queue가 비어있지 않다면
} else {
// 다리가 꽉 찼다면
if (queue.size() == bridgeLength) {
int value = queue.remove(0);
sum = sum - value;
// 다리가 꽉 차지 않았다면
} else {
// 무게 한도가 넘었다면
if (sum+truckWeight > bridgeLimit) {
queue.add(0);
time ++;
// 무게 한도가 넘지 않았다면
} else {
queue.add(truckWeight);
sum = sum + truckWeight;
time ++;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return time + bridgeLength;
}
}
# Deque
Deque는 Stack과 Queue를 합친 자료구조다. Java에서는 Deque인터페이스와 ArrayDeque클래스로 구현한다.
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
deque.addFirst(1);
deque.addLast(2);
deque.addLast(3);
deque.removeFirst(); // 1
deque.removeLast(); // 3
# Hash Table
# 특징
Key-Value로 이루어진 자료구조다.Key와Hash Function으로 데이터를 저장할 주소값을 계산한다.HashFunction(key)=해시 함수의 반환값=해시 값=해시 주소=Hash Table의 인덱스
Hash Table은 보통 고정된배열로 설계한다.- 직접 접근을 하기 때문에 쓰기, 읽기, 검색에
O(1)의 시간 복잡도를 가진다. 충돌(Collision)이 발생하면 검색하는데O(n)의 시간 복잡도가 걸릴 수도 있으므로 충돌이 발생하지 않도록 잘 설계해야한다.
# 구현
public class MyHash {
public class Slot {
String value;
Slot(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHash(Integer size) {
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public int hashFunction(String key) {
// Division 기법
return (int)(key.charAt(0)) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean save(String key, String value) {
Integer address = hashFunction(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
// Overwrite
this.hashTable[address].value = value;
} else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(value);
}
return true;
}
public String get(String key) {
Integer address = hashFunction(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
return this.hashTable[address].value;
} else {
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHash hash = new MyHash(20);
hash.save("Paul", "01055555555");
hash.save("Jonh", "01011111111");
hash.get("Paul"); // 01055555555
}
}
# 충돌
Key에 대한 Hash Value가 동일한 경우 충돌(Collision)이 발생한다.
MyHash hash = new MyHash(20);
// 다른 Key이지만 Hash값 중복이 발생
hash.save("Paul", "01011111111");
hash.save("Paulo", "01022222222");
hash.save("Pogba", "01033333333");
hash.get("Paul"); // 01033333333
따라서 이를 해결하기 위한 별도의 충돌 해결 알고리즘이 필요하다.
Open Hashing: 추가적인 공간을 사용한다.Chaining: 충돌이 일어나면 연결 리스트로 데이터를 추가하여 뒤에 연결한다.
Closed Hashing: 추가적인 공간을 사용하지 않는다.Linear Probing: 충돌이 일어나면 빈 공간이 나오는 다음 공간에 데이터를 추가한다.
Chaining 예제는 다음과 같다.
public class MyHash {
public class Slot {
String value;
String key;
Slot next;
Slot(String key, String value) {
this.value = value;
this.key = key;
this.next = null;
}
}
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHash(Integer size) {
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public int hashFunction(String key) {
return (int)(key.charAt(0)) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean save(String key, String value) {
Integer address = this.hashFunction(key);
// 충돌이 발생했다면
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
Slot findSlot = this.hashTable[address];
Slot prevSlot = this.hashTable[address];
// findSlot이 null이 아닐 때 까지, 즉 끝까지 반복
while (findSlot != null) {
// Hash값이 동일하지만(충돌), key가 내가 찾는 key가 맞는 경우
if (findSlot.key == key) {
findSlot.value = value;
return true;
// Hash 값이 동일하지만(충돌), key가 내가 찾는 key가 아닌 경우
} else {
prevSlot = findSlot;
// 다음 슬롯으로 이동
findSlot = findSlot.next;
}
}
prevSlot.next = new Slot(key, value);
// 중복이 발생하지 않았다면
} else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(key, value);
}
return true;
}
public String get(String key) {
Integer address = this.hashFunction(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
Slot findSlot = this.hashTable[address];
while(findSlot!=null) {
if (findSlot.key == key) {
return findSlot.value;
} else {
findSlot = findSlot.next;
}
}
return null;
} else {
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHash hash = new MyHash(20);
hash.save("Paul", "01011111111");
hash.save("Paulo", "01022222222");
hash.save("Pogba", "01033333333");
System.out.println(hash.getData("Paul")); // 01011111111
}
}
Linear Probing 예제는 다음과 같다.
public class MyHash {
public class Slot {
String value;
String key;
Slot(String key, String value) {
this.value = value;
this.key = key;
}
}
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHash(Integer size) {
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public int hashFunction(String key) {
return (int)(key.charAt(0)) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean save(String key, String value) {
Integer address = this.hashFunction(key);
// 충돌이 발생했다면
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key) {
this.hashTable[address].value = value;
return true;
} else {
Integer curAddress = address + 1;
while (this.hashTable[curAddress] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[curAddress].key == key) {
this.hashTable[curAddress].value = value;
return true;
} else {
// 다음 index로 이동
curAddress++;
if (curAddress >= this.hashTable.length) {
return false;
}
}
}
this.hashTable[curAddress] = new Slot(key, value);
}
// 충돌이 발생하지 않았다면
} else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(key, value);
}
return true;
}
public String get(String key) {
Integer address = this.hashFunction(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key) {
return this.hashTable[address].value;
} else {
Integer currAddress = address + 1;
while (this.hashTable[currAddress] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[currAddress] != null) {
return this.hashTable[currAddress].value;
} else {
currAddress++;
if (currAddress >= this.hashTable.length) {
return null;
}
}
}
return null;
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHash hash = new MyHash(20);
hash.save("Paul", "01011111111");
hash.save("Paulo", "01022222222");
hash.save("Pogba", "01033333333");
System.out.println(hash.getData("Paul")); // 01011111111
}
}
충돌을 개선하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
- 더 효율적인
Hash Function을 정의한다. Hash Table의 저장공간을 확대한다.
Java에서는 Map인터페이스를 사용한다.
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
<Integer, String> map = new HashMap();
map.put(1, "Ronaldo");
map.put(2, "Kane");
map.put(3, "Paul");
map.get(2);
# 완주하지 못한 선수
완주하지 못한 선수
수많은 마라톤 선수들이 마라톤에 참여하였습니다. 단 한 명의 선수를 제외하고는 모든 선수가 마라톤을 완주하였습니다.
마라톤에 참여한 선수들의 이름이 담긴 배열 participant와 완주한 선수들의 이름이 담긴 배열 completion이 주어질 때, 완주하지 못한 선수의 이름을 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
- 제한사항
- 마라톤 경기에 참여한 선수의 수는 1명 이상 100,000명 이하입니다.
- completion의 길이는 participant의 길이보다 1 작습니다.
- 참가자의 이름은 1개 이상 20개 이하의 알파벳 소문자로 이루어져 있습니다.
- 참가자 중에는 동명이인이 있을 수 있습니다.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] participant, String[] completion) {
HashMap<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap();
for (String person: participant) {
hashMap.put(person, hashMap.getOrDefault(person, 0) + 1);
}
for (String person: completion) {
hashMap.put(person, hashMap.get(person) - 1);
}
for (String key: hashMap.keySet()) {
if (hashMap.get(key) != 0) {
return key;
}
}
return "";
}
}
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] participant, String[] completion) {
Arrays.sort(participant);
Arrays.sort(completion);
for (int i=0; i<completion.length; i++) {
if (!completion[i].equals(participant[i])) {
return participant[i];
}
}
return participant[participant.length - 1];
}
}
# 전화번호 목록
전화번호 목록
전화번호부에 적힌 전화번호 중, 한 번호가 다른 번호의 접두어인 경우가 있는지 확인하려 합니다. 전화번호가 다음과 같을 경우, 구조대 전화번호는 영석이의 전화번호의 접두사입니다.
- 구조대 : 119
- 박준영 : 97 674 223
- 지영석 : 11 9552 4421
전화번호부에 적힌 전화번호를 담은 배열 phone_book 이 solution 함수의 매개변수로 주어질 때, 어떤 번호가 다른 번호의 접두어인 경우가 있으면 false를 그렇지 않으면 true를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public boolean solution(String[] phoneBook) {
boolean answer = true;
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap();
for (int i=0; i<phoneBook.length; i++) {
map.put(phoneBook[i], i);
}
for (int i=0; i<phoneBook.length; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<phoneBook[i].length(); j++) {
if (map.containsKey(phoneBook[i].substring(0, j))) {
return false;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}
# 위장
위장
스파이들은 매일 다른 옷을 조합하여 입어 자신을 위장합니다.
예를 들어 스파이가 가진 옷이 아래와 같고 오늘 스파이가 동그란 안경, 긴 코트, 파란색 티셔츠를 입었다면 다음날은 청바지를 추가로 입거나 동그란 안경 대신 검정 선글라스를 착용하거나 해야 합니다.
| 종류 | 이름 |
|---|---|
| 얼굴 | 동그란 안경, 검정 선글라스 |
| 상의 | 파란색 티셔츠 |
| 하의 | 청바지 |
| 겉옷 | 긴 코트 |
- 제한사항
- clothes의 각 행은 [의상의 이름, 의상의 종류]로 이루어져 있습니다.
- 스파이가 가진 의상의 수는 1개 이상 30개 이하입니다.
- 같은 이름을 가진 의상은 존재하지 않습니다.
- clothes의 모든 원소는 문자열로 이루어져 있습니다.
- 모든 문자열의 길이는 1 이상 20 이하인 자연수이고 알파벳 소문자 또는 '_' 로만 이루어져 있습니다.
- 스파이는 하루에 최소 한 개의 의상은 입습니다.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(String[][] clothes) {
int answer = 1;
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap();
for (int i=0; i<clothes.length; i++) {
if(!map.containsKey(clothes[i][1])) {
map.put(clothes[i][1], 1);
} else {
map.put(clothes[i][1], map.get(clothes[i][1])+1);
}
}
for(String key: map.keySet()) {
answer = answer * (map.get(key)+1);
}
return answer-1;
}
}
# Tree
# Tree의 구성요소
- Node
- Edge
- Root Node
- Leaf Node
- Level 0 ~ Level N
- Depth N
# 이진 트리
- 자식이 0, 1, 2개
# 완전 이진 트리
완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree)는 다음과 같은 특성을 갖는다.
- 레벨의 왼쪽에서부터 순차적으로 노드를 추가한다.
- 레벨 N이 다 채워져야만 레벨 N+1에 노드를 추가할 수 있다.
# 이진 검색 트리
BST(Binary Serach Tree, 이진 검색 트리)는 Left < Root < Right라는 특성을 갖는 이진 트리이며, 빠른 검색(O(logn))에 사용된다.
# 구현
public class BST {
Node root;
public class Node {
int element;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.element = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
public BST() {
this.root = null;
}
// 삽입
public void insertNode(int element) {
// CASE 1: Node가 하나도 없을 때
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = new Node(element);
// CASE 2: Node가 하나 이상 들어있을 때
} else {
Node current = this.root;
while (true) {
// CASE 2-1: 데이터가 현재 노드보다 작으면 왼쪽 노드에 삽입해야한다.
if (element < current.element) {
// CASE 2-1-1: 왼쪽 노드가 null이 아니면 왼쪽 노드를 current 노드로 설정한다.
if (current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
// CASE 2-1-1: 왼쪽 노드가 null이면 왼쪽 노드에 새로운 노드를 삽입하고 반복문을 종료한다.
} else {
current.left = new Node(element);
break;
}
// CASE 2-2: 데이터가 현재 노드보다 크면 오른쪽 노드에 삽입해야 한다.
} else {
// CASE 2-2-1: 오른쪽 노드가 null이 아니면 오른쪽 노드를 temp 노드로 설정한다.
if (current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
// CASE 2-2-2: 오른쪽 노드가 null이면 오른쪽 노드에 새로운 노드를 삽입하고 반복문을 종료한다.
} else {
current.right = new Node(element);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 검색
public Node search(int element) {
// CASE 1: Node가 하나도 없을 때
if (this.root == null) {
return null;
// CASE 2: Node가 하나 이상 있을 때
} else {
Node current = this.root;
while (current != null) {
// CASE 2-1: 현재 노드가 찾는 노드일 때
if (current.element == element) {
return current;
// CASE 2-2: 찾는 노드가 현재 노드보다 작을 때
} else if (element < current.element) {
current = current.left;
// CASE 2-3: 찾는 노드가 현재 노드보다 클 때
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BST tree = new BST();
System.out.println("================ 삽입 ================");
tree.insertNode(5);
tree.insertNode(3);
tree.insertNode(9);
tree.insertNode(1);
tree.insertNode(7);
tree.insertNode(10);
tree.insertNode(8);
System.out.println(tree.root.element); // 5
System.out.println(tree.root.left.element); // 3
System.out.println(tree.root.right.element); // 9
System.out.println(tree.root.left.left.element); // 1
System.out.println(tree.root.right.left.element); // 7
System.out.println(tree.root.right.right.element); // 10
System.out.println(tree.root.right.left.right.element); // 8
System.out.println("================ 삭제 ================");
Node target = null;
target = tree.search(8);
System.out.println(target.element); // 8
target = tree.search(3);
System.out.println(target.element); // 3
target = tree.search(10);
System.out.println(target.element); // 10
target = tree.search(2);
System.out.println(target); // null
}
}
# 삭제 시 고려사항
- 삭제할 노드의 자식이 없는 경우
- 삭제할 노드가 자식이 1개 있는 경우
- 자식 한개가 왼쪽에 있는 경우
- 자식 한개가 오른쪽에 있는 경우
- 삭제할 노드가 자식이 2개가 있는 경우
- 오른쪽 트리의 가장 왼쪽 요소 또는 왼쪽 트리의 가장 오른쪽 요소로 대체
# 이진트리 순회
public class BST {
Node root;
public class Node {
int element;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.element = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
public BST() {
this.root = null;
}
public void preorder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.element + " ");
if(root.left != null) preorder(root.left);
if(root.right != null) preorder(root.right);
}
}
public void inorder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
if(root.left != null) inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.element + " ");
if(root.right != null) inorder(root.right);
}
}
public void postorder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
if(root.left != null) postorder(root.left);
if(root.right != null) postorder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.element + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BST tree = new BST();
tree.insertNode(5);
tree.insertNode(3);
tree.insertNode(9);
tree.insertNode(1);
tree.insertNode(7);
tree.insertNode(10);
tree.insertNode(8);
tree.preorder(tree.root); // 5 3 1 9 7 8 10
tree.inorder(tree.root); // 1 3 5 7 8 9 10
tree.postorder(tree.root); // 1 3 8 7 10 9 5
}
}
# Priority Quene & Heap
# Proirity Queue
- 들어온 순서에 상관없이 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나오는 자료구조
- 우선순위 큐는 보통
힙(Heap)이라는 자료구조로 구현한다. - Java에서는
PriorityQueue클래스로 구현할 수 있다.
# Heap
- 최대값과 최소값을 빠르게 찾기 위한
완전이진트리 - 힙의 특징
- 최대 힙, 최소 힙이 존재한다.
- 최대 힙의 경우, 부모 노드는 자식 노드들보다 값이 크거나 같다.
- 최소 힙의 경우, 부모 노드는 자식 노드들보다 값이 작거나 같다.
- 즉, 루트 노드는 값이 가장 크거나 가장 작다.
- 데이터 삽입 방법
- 완전이진트리 끝에 노드 추가
- 추가된 노드의 값이 부모 노드 값보다 크면 위로 계속 스왑
- 데이터 삭제
- 힙의 삭제는
루트 노드를 삭제하는 것이 일반적 - 데이터가 삭제되면 가장 높은 레벨의 끝 노드를 루트 노드로 옮긴다.
- 그 다음 두 자식노드와 값을 비교하여 큰 노드와 스왑
Collections.swap()을 사용한다.
- 힙의 삭제는
- 힙의 구현
- 보통
배열을 사용한다. 인덱스 0번은 비워둔다.- 부모 노드의 인덱스 번호 = 자식 노드의 인덱스 번호 / 2
- 왼쪽 자식의 인덱스 번호 = 부모 노드의 인덱스 번호 * 2
- 오른쪽 자식의 인덱스 번호 = (부모 노드의 인덱스 번호 * 2) + 1
- 보통
# 최소힙
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
heap.add(3);
heap.add(9);
heap.add(5);
heap.add(6);
heap.add(20);
heap.add(16);
heap.add(7);
System.out.println(heap.remove()); // 3
System.out.println(heap.remove()); // 5
System.out.println(heap.remove()); // 6
# 최대힙
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
heap.add(3);
heap.add(9);
heap.add(5);
heap.add(6);
heap.add(20);
heap.add(16);
heap.add(7);
System.out.println(heap.poll()); // 20
System.out.println(heap.poll()); // 16
System.out.println(heap.poll()); // 9
# Comparator
class Student {
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
PriorityQueue<Student> heap = new PriorityQueue(new Comparator() {
@Overide
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
return s1.age - os.age;
}
});
head.add(new Student("Paul", 30));
head.add(new Student("John", 10));
head.add(new Student("Son", 20));
# Comparable
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student target) {
return this.age - target.age;
}
}
PriorityQueue<Student> heap = new PriorityQueue();
head.add(new Student("Paul", 30));
head.add(new Student("John", 10));
head.add(new Student("Son", 20));
# 더 맵게
더 맵게
매운 것을 좋아하는 Leo는 모든 음식의 스코빌 지수를 K 이상으로 만들고 싶습니다. 모든 음식의 스코빌 지수를 K 이상으로 만들기 위해 Leo는 스코빌 지수가 가장 낮은 두 개의 음식을 아래와 같이 특별한 방법으로 섞어 새로운 음식을 만듭니다.
섞은 음식의 스코빌 지수 = 가장 맵지 않은 음식의 스코빌 지수 + (두 번째로 맵지 않은 음식의 스코빌 지수 * 2)
Leo는 모든 음식의 스코빌 지수가 K 이상이 될 때까지 반복하여 섞습니다. Leo가 가진 음식의 스코빌 지수를 담은 배열 scoville과 원하는 스코빌 지수 K가 주어질 때, 모든 음식의 스코빌 지수를 K 이상으로 만들기 위해 섞어야 하는 최소 횟수를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
제한 사항
- scoville의 길이는 2 이상 1,000,000 이하입니다.
- K는 0 이상 1,000,000,000 이하입니다.
- scoville의 원소는 각각 0 이상 1,000,000 이하입니다.
- 모든 음식의 스코빌 지수를 K 이상으로 만들 수 없는 경우에는 -1을 return 합니다.
입출력 예
| scoville | K | return |
|---|---|---|
| [1, 2, 3, 9, 10, 12] | 7 | 2 |
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] scoville, int K) {
int count = 0;
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue();
for (int i=0; i<scoville.length; i++) {
heap.add(scoville[i]);
}
while (heap.peek() < K) {
if (heap.size() == 1) break;
int sum = heap.remove() + (heap.remove()*2);
heap.add(sum);
count++;
}
if (heap.peek() < K) return -1;
return count;
}
}
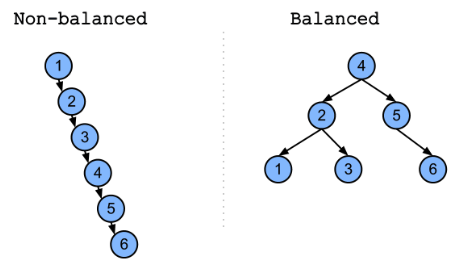
# Balanced Tree
- Binary Search Tree는 좌우 균형이 맞지 않으면 최악의 경우
O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 갖게 된다. - Balanced Tree는 삽입, 삭제, 변경 시 필요하면 균형을 맞춰서
O(logn)의 시간 복잡도를 갖게 한다. - Balanced Tree에는 AVL Tree, 2-3 Tree, 2-3-4 Tree, Red-Black Tree, B-Tree 등이 있다.
# B-Tree
- 하나의 노드에 여러 자료가 배치되는 자료구조
- 한 노드에 N개의 자료가 저장되면 N차 B-tree라고 한다.
- 한 노드에 N개의 자료가 저장된다면 그 노드의 자식 수는 N+1개 여야한다.
# Graph
# 구성 요소
- Vertex
- Edge
- Adjacent Vertex(인접 노드)
- Degree(차수): 인접한 edge의 수
# 그래프의 종류
- 무방향 그래프
- 방향 그래프
- 가중치 그래프
# 그래프의 구현
그래프는 두 가지 방법으로 구현할 수 있다.
- 인접 행렬
- 인접 리스트
# 인접 행렬
그래프를 인접행렬로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
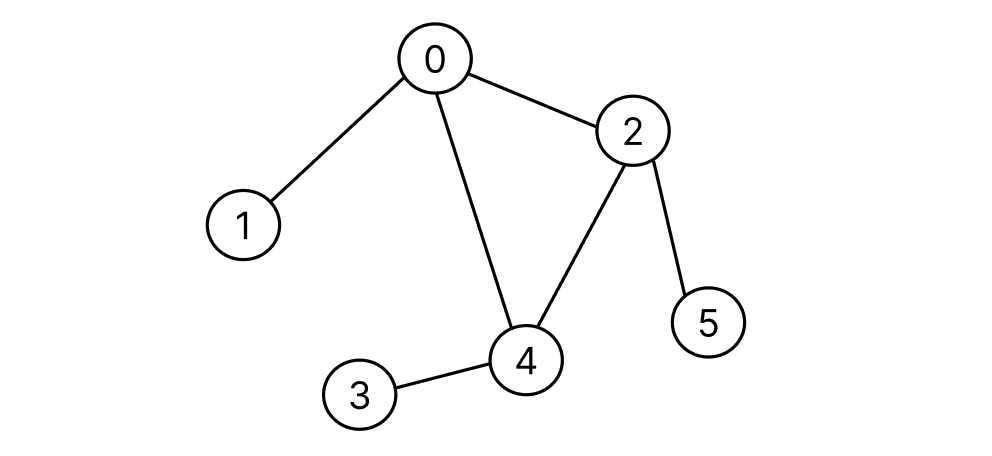
int[][] graph = {
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}
};
graph[0][1]은 0번 Vertext와 1번 Vertext 사이에 Edge가 존재함을 의미한다.
# 인접 리스트
그래프를 인접 리스트로 구현하면 다음과 같다.

HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new HashMap();
graph.put(0, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4)));
graph.put(1, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0)));
graph.put(2, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 4, 5)));
graph.put(3, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(4)));
graph.put(4, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 2, 3)));
graph.put(5, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(2)));
# 그래프 탐색
시작점으로부터 모든 정점을 한번씩 방문하는 방법을 그래프 탐색이라고 한다.
- DFS
- BFS
# DFS(깊이 우선 탐색)
DFS는 Stack 또는 재귀(Recursion)을 통해 구현할 수 있다.
인접 행렬을 Stack으로 풀면 다음과 같다.
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] graph = {
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}
};
System.out.println(bfs(graph, 0));
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> bfs(int[][] graph, int start) {
Stack<Integer> needVisit = new Stack<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> visited = new ArrayList<Integer>();
needVisit.push(start);
while(needVisit.size() > 0) {
// 방문이 필요한 노드 하나를 가져와서
int node = needVisit.pop();
// 방문하지 않았다면
if (!visited.contains(node)) {
// 방문하고
visited.add(node);
// 인접한 노드 중에서 방문하지 않는 노드를 needVisit에 넣는다
for (int i=0; i<graph[node].length; i++) {
if (graph[node][i] == 1 && !visited.contains(i)) {
needVisit.push(i);
}
}
}
}
return visited;
}
}
인접 행렬을 재귀(Recursion)로 풀면 다음과 같다.
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] graph = {
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}
};
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[graph.length];
List<Integer> visited = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(graph, 0, isVisited, visited);
System.out.println(visited); // [0, 1, 2, 4, 3, 5]
}
public static void dfs(int[][] graph, int start, boolean[] isVisited, List<Integer> visited) {
isVisited[start] = true;
visited.add(start);
// 인접한 노드 중에서
for (int i=0; i<graph[start].length; i++) {
// 정점 start에서 정점 i로의 경로가 존재하고, 정점 i를 방문하지 않았다면,
if (graph[start][i] == 1 && isVisited[i] == false) {
dfs(graph, i, isVisited, visitedList);
}
}
}
}
인접 리스트를 Stack으로 풀어보자.
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new HashMap();
graph.put(0, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4)));
graph.put(1, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0)));
graph.put(2, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 4, 5)));
graph.put(3, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(4)));
graph.put(4, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 2, 3)));
graph.put(5, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(2)));
System.out.println(dfs(graph, 0)); // [0, 4, 3, 2, 5, 1]
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> dfs(HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph, int start) {
// 1개의 Queue, 1개의 Stack을 사용한다.
ArrayList<Integer> visited = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> needVisit = new Stack<Integer>();
needVisit.push(start);
while (needVisit.size() > 0) {
Integer node = needVisit.pop();
// 방문을 안했다면
if (!visited.contains(node)) {
visited.add(node);
ArrayList<Integer> adjacent = graph.get(node);
for(int i=0; i<adjacent.size(); i++) {
needVisit.push(adjacent.get(i));
}
}
}
return visited;
}
}
인접 리스트를 재귀(Recursion)으로 풀면 다음과 같다.
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new HashMap();
graph.put(0, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4)));
graph.put(1, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0)));
graph.put(2, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 4, 5)));
graph.put(3, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(4)));
graph.put(4, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 2, 3)));
graph.put(5, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(2)));
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[graph.size()];
ArrayList<Integer> visitedList = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(graph, 0, isVisited, visitedList);
System.out.println(visitedList);
}
public static void dfs(HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph, int start, boolean[] isVisited, ArrayList<Integer> visitedList) {
isVisited[start] = true;
visitedList.add(start);
ArrayList<Integer> adjacent = graph.get(start);
for (int node: adjacent) {
if (isVisited[node] == false) {
dfs(graph, node, isVisited, visitedList);
}
}
}
}
# BFS(너비 우선 탐색)
BFS는 Queue를 사용하면 된다.
인접 행렬을 Queue로 해결해보자.
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] graph = {
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}
};
System.out.println(bfs(graph, 0)); // [0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 3]
System.out.println(bfs(graph, 1)); // [1, 0, 2, 4, 5, 3]
System.out.println(bfs(graph, 2)); // [2, 0, 4, 5, 1, 3]
System.out.println(bfs(graph, 3)); // [3, 4, 0, 2, 1, 5]
System.out.println(bfs(graph, 4)); // [4, 0, 2, 3, 1, 5]
System.out.println(bfs(graph, 5)); // [5, 2, 0, 4, 1, 3]
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> bfs(int[][] graph, int start) {
ArrayList<Integer> needVisit = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> visited = new ArrayList<>();
needVisit.add(start);
while(needVisit.size() > 0) {
int node = needVisit.remove(0);
// node를 방문하지 않았다면
if (!visited.contains(node)) {
// node를 방문하고
visited.add(node);
for (int i=0; i< graph[node].length; i++) {
// 인접한 노드 중에서 방문하지 않는 노드만 needVisit에 넣는다.
if (graph[node][i] == 1 && !visited.contains(i)) {
needVisit.add(i);
}
}
}
}
return visited;
}
}
인접 리스트를 Queue로 해결해보자.
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new HashMap();
graph.put(0, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 4)));
graph.put(1, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0)));
graph.put(2, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 4, 5)));
graph.put(3, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(4)));
graph.put(4, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 2, 3)));
graph.put(5, new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(2)));
System.out.println(bfs(graph, 0)); // [0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 3]
}
public static ArrayList<Integer> bfs(HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph, Integer start) {
// 2개의 Queue를 사용한다.
ArrayList<Integer> visited = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> needVisit = new ArrayList<Integer>();
needVisit.add(start);
while(needVisit.size() > 0) {
Integer node = needVisit.remove(0);
// 방문을 안했다면
if (!visited.contains(node)) {
visited.add(node);
needVisit.addAll(graph.get(node));
}
}
return visited;
}
}
# 네트워크
네트워크
네트워크란 컴퓨터 상호 간에 정보를 교환할 수 있도록 연결된 형태를 의미합니다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터 A와 컴퓨터 B가 직접적으로 연결되어있고, 컴퓨터 B와 컴퓨터 C가 직접적으로 연결되어 있을 때 컴퓨터 A와 컴퓨터 C도 간접적으로 연결되어 정보를 교환할 수 있습니다. 따라서 컴퓨터 A, B, C는 모두 같은 네트워크 상에 있다고 할 수 있습니다.
컴퓨터의 개수 n, 연결에 대한 정보가 담긴 2차원 배열 computers가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 네트워크의 개수를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성하시오.
- 입출력 예제
| n | computers | return |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]] | 2 |
| 3 | [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 1]] | 1 |
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[][] computers) {
int networkCount = 0;
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[n];
// 모든 노드에 대해서 dfs 수행
for (int i=0; i<computers.length; i++) {
if (isVisited[i] == false) {
networkCount ++;
dfs(computers, i, isVisited);
}
}
return networkCount;
}
public void dfs(int[][] graph, int start, boolean[] isVisited) {
isVisited[start] = true;
for (int i=0; i<graph[start].length; i++) {
if (graph[start][i] == 1 && isVisited[i] == false) {
dfs(graph, i, isVisited);
}
}
}
}
# 단어 변환
단어 변환
두 개의 단어 begin, target과 단어의 집합 words가 있습니다. 아래와 같은 규칙을 이용하여 begin에서 target으로 변환하는 가장 짧은 변환 과정을 찾으려고 합니다.
- 한 번에 한 개의 알파벳만 바꿀 수 있습니다.
- words에 있는 단어로만 변환할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 begin이 "hit", target가 "cog", words가 ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]라면 "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog"와 같이 4단계를 거쳐 변환할 수 있습니다.
두 개의 단어 begin, target과 단어의 집합 words가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 최소 몇 단계의 과정을 거쳐 begin을 target으로 변환할 수 있는지 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
int answer = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
boolean[] isVisited;
public int solution(String begin, String target, String[] words) {
isVisited = new boolean[words.length];
dfs(begin, target, words, 0);
if (answer == Integer.MAX_VALUE) return 0;
return answer;
}
public void dfs(String begin, String target, String[] words, int depth) {
if (depth > words.length)
return;
if (begin.equals(target)) {
answer = Math.min(answer, depth);
return;
}
for (int i=0; i<words.length; i++) {
if (isChangeable(begin, words[i]) && !isVisited[i]) {
isVisited[i] = true;
dfs(words[i], target, words, depth+1);
isVisited[i] = false;
}
}
}
// 문자가 하나만 다른지 확인
public boolean isChangeable(String str1, String str2) {
int diffCount = 0;
for (int i=0; i<str1.length(); i++) {
if (str1.charAt(i) != str2.charAt(i)) diffCount ++;
}
return diffCount == 1;
}
}
# 최단 경로 알고리즘 (다익스트라)
- 하나의 노드에서 다른 모든 노드들까지의 최단 거리를 구하는 알고리즘
- 이전에 계산한 값을 재사용한다는 점에서 다이나믹 프로그래밍으로 분류하기도 한다.
- 현재 노드에서 가장 짧은 거리의 노드를 선택한다는 점에서 그리디 알고리즘으로 분류하기도 한다.
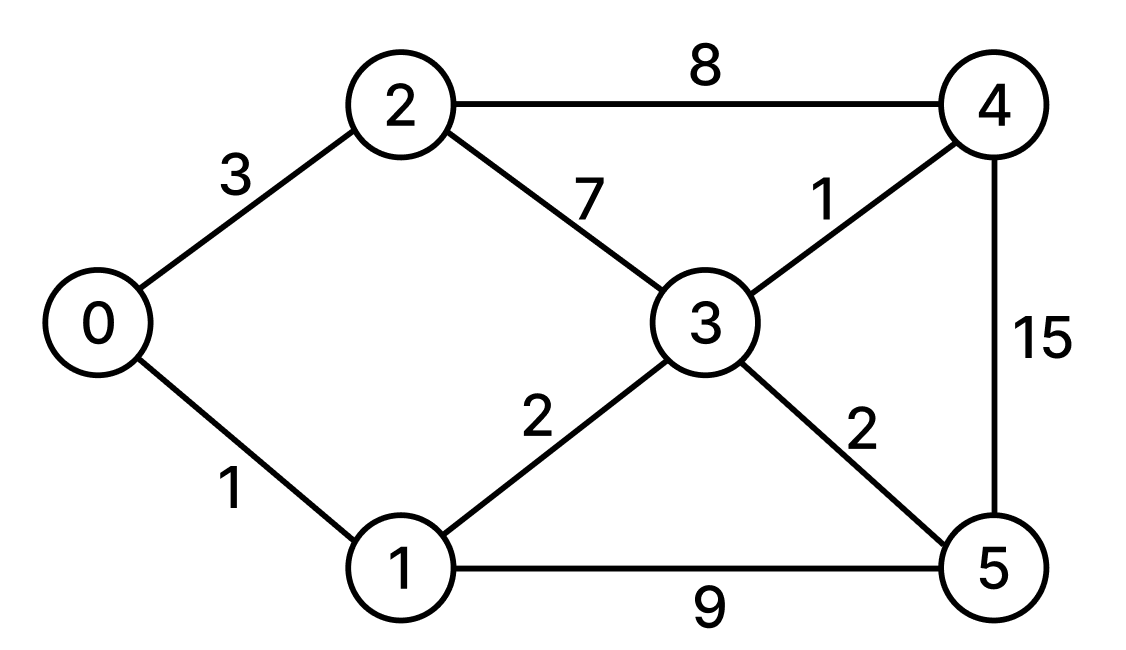
위와 같은 그래프가 있고 시작정점이 3일 때, 다익스트라 알고리즘은 다음과 같이 동작한다.
먼저 최단거리 배열과 방문여부 배열을 초기화한다.
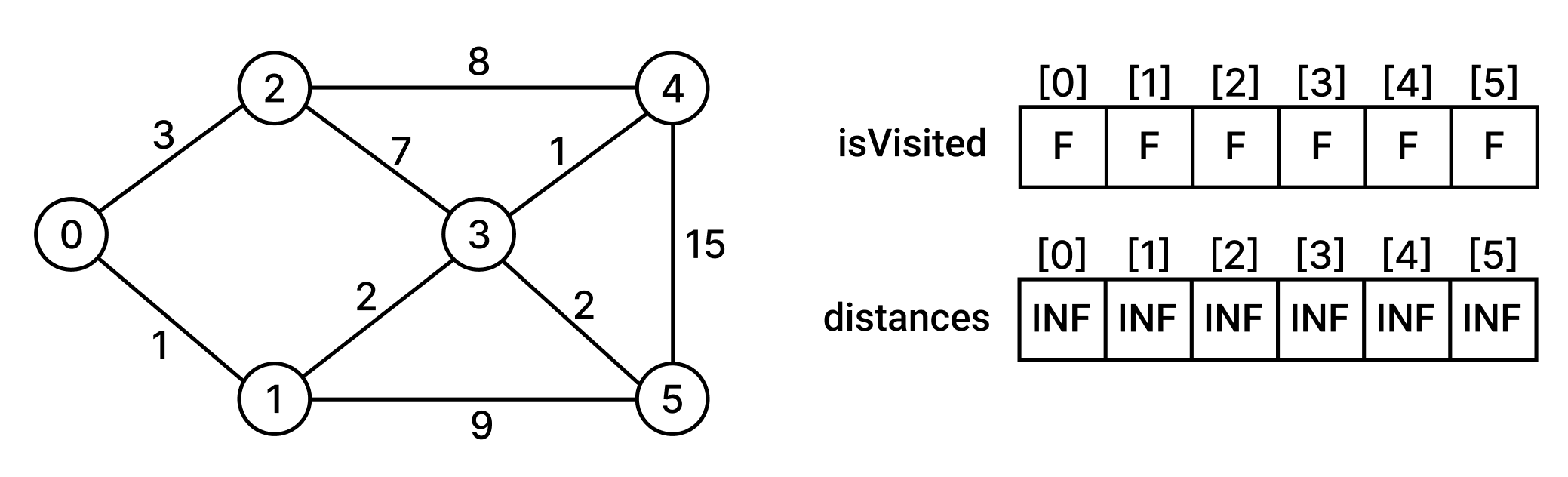
그리고 시작정점에 대한 최단거리배열을 초기화한다.
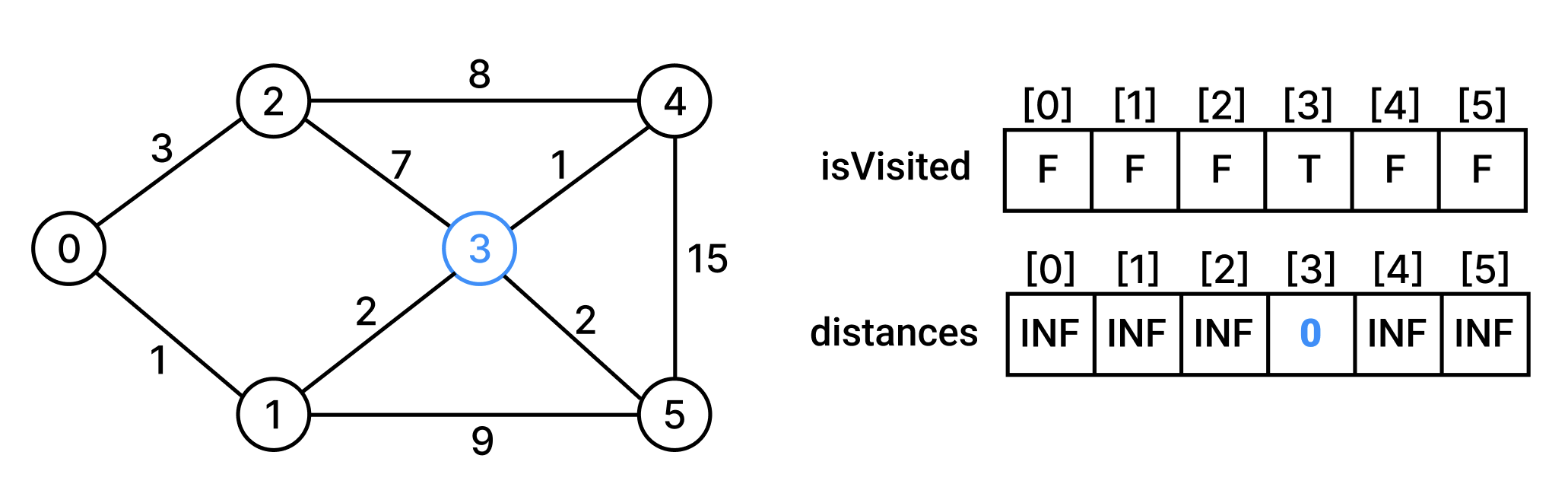
시작정점을 방문한 후, 시작정점과 인접한 정점에 대해서 최단거리배열을 갱신한다.
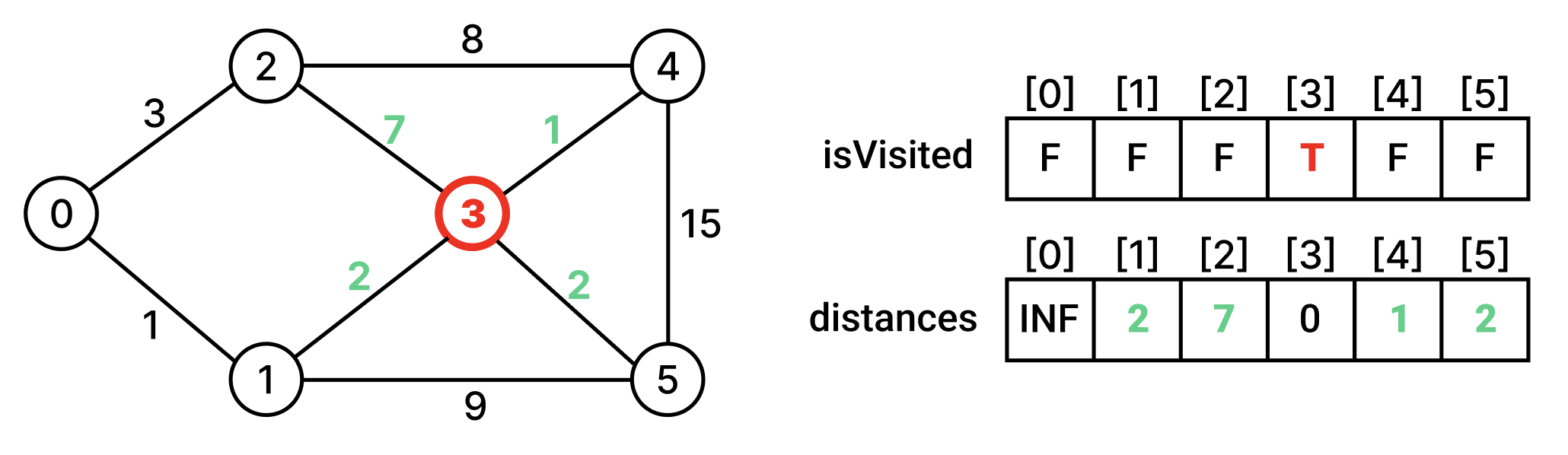
방문하지 않은 인접 정점 중에서 최단거리인 정점을 찾아 방문한다. 그리고 그 정점과 인접한 정점들의 최단거리 배열을 갱신한다.
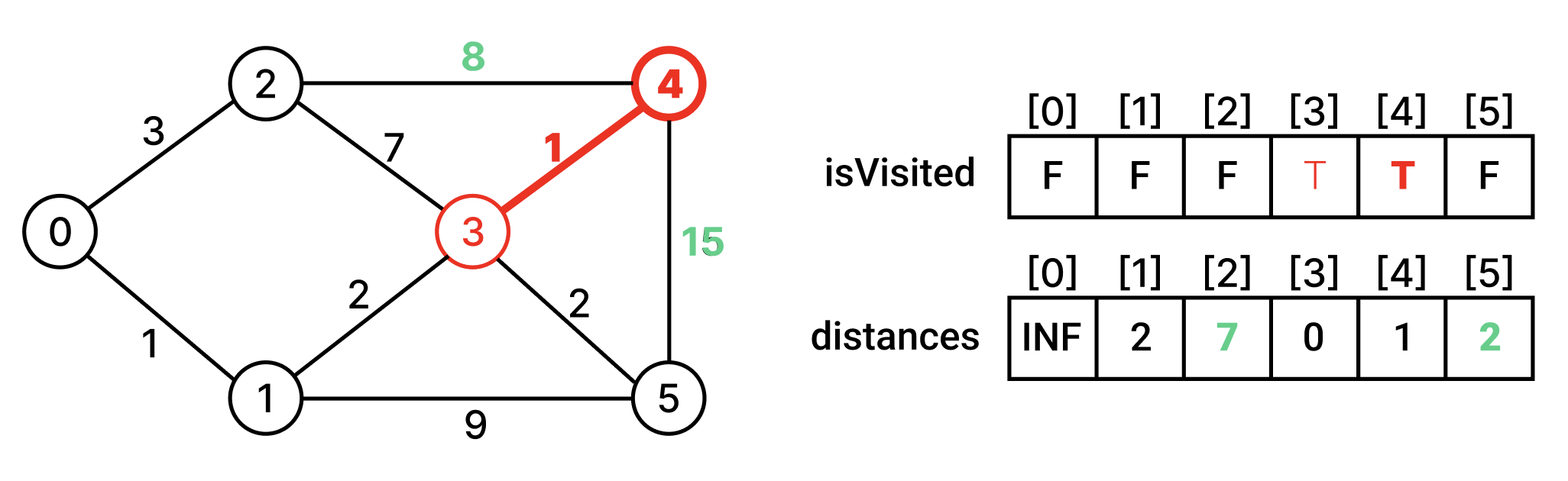
방문하지 않은 인접 정점 중에서 최단거리인 정점을 찾아 방문한다. 그리고 그 정점과 인접한 정점들의 최단거리 배열을 갱신한다.
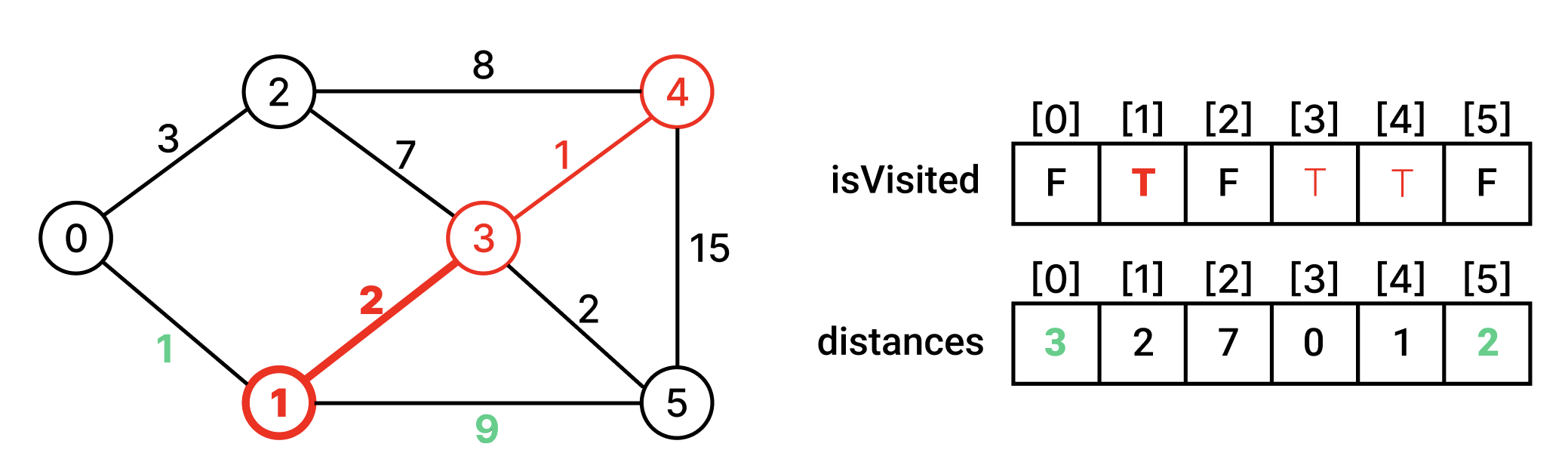
방문하지 않은 인접 정점 중에서 최단거리인 정점을 찾아 방문한다. 그리고 그 정점과 인접한 정점들의 최단거리 배열을 갱신한다.
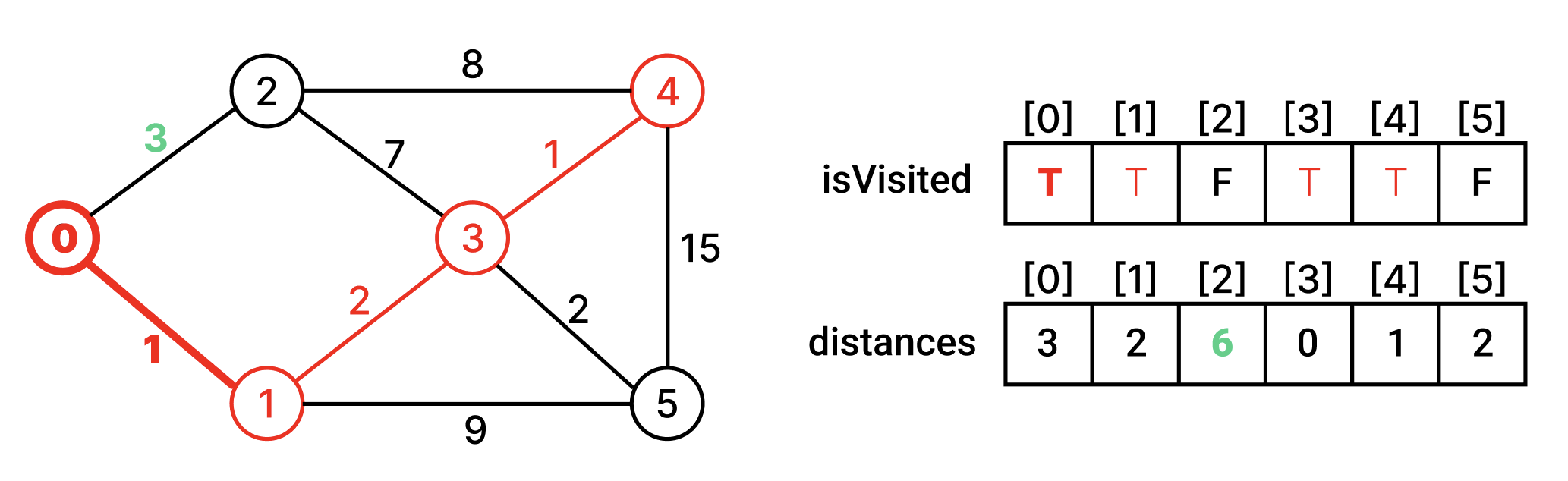
방문하지 않은 인접 정점 중에서 최단거리인 정점을 찾아 방문한다. 그리고 그 정점과 인접한 정점들의 최단거리 배열을 갱신한다.
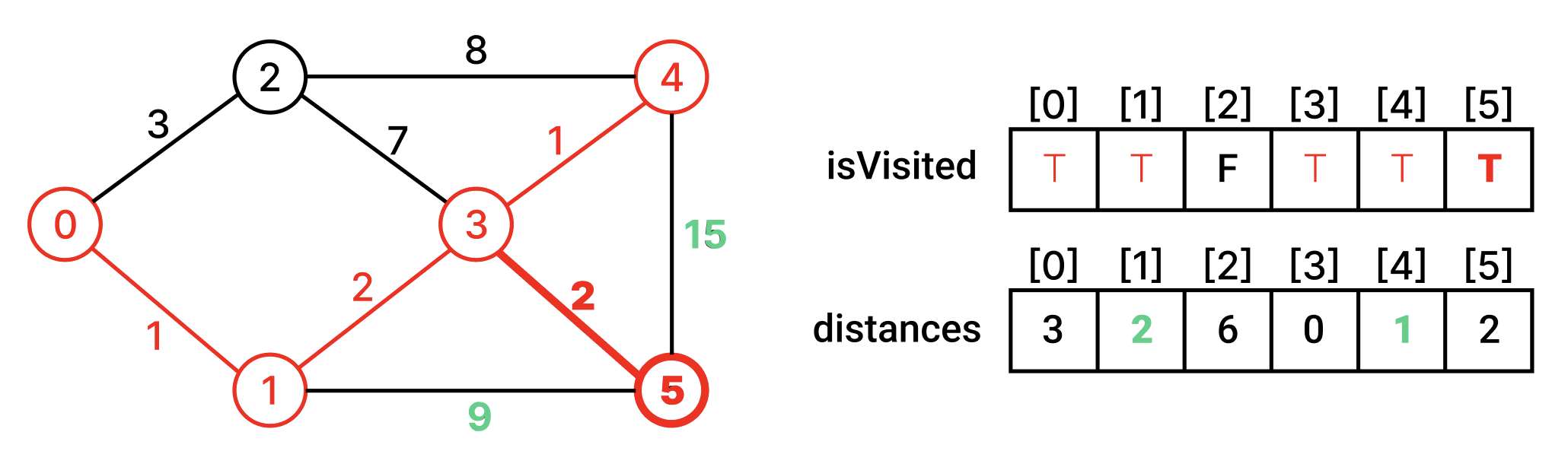
방문하지 않은 인접 정점 중에서 최단거리인 정점을 찾아 방문한다. 그리고 그 정점과 인접한 정점들의 최단거리 배열을 갱신한다.
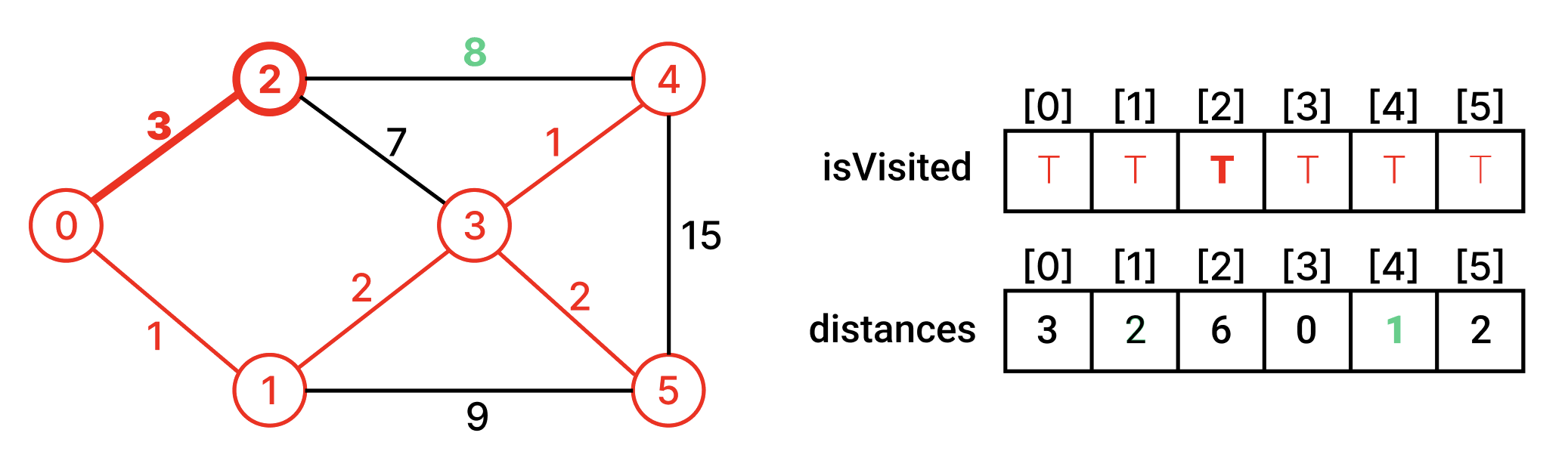
# 풀이 1. 이차원 배열
가중치 인접행렬이라는 이차원 배열을 사용할 수 있다.
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph(6);
graph.input(0, 1, 1);
graph.input(0, 2, 3);
graph.input(1, 0, 1);
graph.input(1, 3, 2);
graph.input(1, 5, 9);
graph.input(2, 0, 3);
graph.input(2, 3, 7);
graph.input(2, 4, 8);
graph.input(3, 1, 2);
graph.input(3, 2, 7);
graph.input(3, 4, 1);
graph.input(3, 5, 2);
graph.input(4, 2, 8);
graph.input(4, 3, 1);
graph.input(4, 5, 15);
graph.input(5, 1, 9);
graph.input(5, 3, 2);
graph.input(5, 4, 15);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(graph.dijkstra(0))); // [0, 1, 3, 3, 4, 5]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(graph.dijkstra(1))); // [1, 0, 4, 2, 3, 4]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(graph.dijkstra(2))); // [3, 4, 0, 6, 7, 8]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(graph.dijkstra(3))); // [3, 2, 6, 0, 1, 2]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(graph.dijkstra(4))); // [4, 3, 7, 1, 0, 3]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(graph.dijkstra(5))); // [5, 4, 8, 2, 3, 0]
}
}
class Graph {
private int n; // Node의 수
private int[][] graph; // 그래프
public Graph(int n) {
this.n = n;
this.graph = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
graph[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public void input(int i, int j, int weight) {
graph[i][j] = weight;
graph[j][i] = weight;
}
public int[] dijkstra(int start) {
// 거리 저장 배열 생성
int[] distance = new int[n];
// 거리 저장 배열 무한대로 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < distance.length; i++) {
distance[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// 방문 여부 확인 배열 생성
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[n];
// 시작 노드 초기화
distance[start] = 0;
isVisited[start] = true;
// 시작 노드와 연결된 노드들의 distance 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 방문하지 않았고, 시작 노드와 연결되어있다면
if (!isVisited[i] && graph[start][i] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
distance[i] = graph[start][i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minIdx = -1;
// 현재 노드에서 최소 거리의 노드 찾기
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// j 노드를 방문하지 않았고, j 노드가 가장 가깝다면
if (!isVisited[j] && distance[j] < min) {
min = distance[j];
minIdx = j;
}
}
// 현재 노드에서 최단거리 노드 방문
isVisited[minIdx] = true;
// 다른 노드를 통한 경로보다 거리가 더 가까운지 비교
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
// k번 노드에 방문하지 않았고 && k번 노드로의 경로가 있고 &&
if (!isVisited[k] && graph[minIdx][k] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && distance[minIdx] + graph[minIdx][k] < distance[k]) {
distance[k] = distance[minIdx] + graph[minIdx][k];
}
}
}
return distance;
}
public void printGraph() {
System.out.println("=========================");
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++)
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(graph[i]));
System.out.println("=========================");
}
}
시간 복잡도 O(n^2)
# 풀이 2. 우선순위 큐
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, ArrayList<Edge>> graph = new HashMap<>();;
graph.put(0, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge(2, 3), new Edge(1, 1))));
graph.put(1, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge(0, 1), new Edge(3, 2), new Edge(5, 9))));
graph.put(2, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge(0, 3), new Edge(3, 6), new Edge(4, 8))));
graph.put(3, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge(1, 2), new Edge(2, 6), new Edge(4, 1), new Edge(5, 2))));
graph.put(4, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge(2, 8), new Edge(3, 1), new Edge(5, 15))));
graph.put(5, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge(1, 9), new Edge(3, 2), new Edge(4, 15))));
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.dijkstra(graph, 0)); // {0=0, 1=1, 2=3, 3=3, 4=4, 5=5}
System.out.println(solution.dijkstra(graph, 1)); // {0=1, 1=0, 2=4, 3=2, 4=3, 5=4}
System.out.println(solution.dijkstra(graph, 2)); // {0=3, 1=4, 2=0, 3=6, 4=7, 5=8}
System.out.println(solution.dijkstra(graph, 3)); // {0=3, 1=2, 2=6, 3=0, 4=1, 5=2}
System.out.println(solution.dijkstra(graph, 4)); // {0=4, 1=3, 2=7, 3=1, 4=0, 5=3}
System.out.println(solution.dijkstra(graph, 5)); // {0=5, 1=4, 2=8, 3=2, 4=3, 5=0}
}
}
class Solution {
public Solution() {
}
public Map<Integer, Integer> dijkstra(Map<Integer, ArrayList<Edge>> graph, int start) {
// 거리 저장 Map 생성 & 초기화
Map<Integer, Integer> distances = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer key : graph.keySet()) distances.put(key, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// start 노드 추가
distances.put(start, 0);
Edge edgeNode;
Integer currentDistance;
Integer currentNode;
ArrayList<Edge> nodeList;
Integer adjacent;
Integer weight;
Integer distance;
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.add(new Edge(start, 0));
while (priorityQueue.size() > 0) {
edgeNode = priorityQueue.remove();
currentDistance = edgeNode.distance;
currentNode = edgeNode.destination;
if (distances.get(currentNode) < currentDistance) continue;
nodeList = graph.get(currentNode);
for (Edge node : nodeList) {
adjacent = node.destination;
weight = node.distance;
distance = weight + currentDistance;
if (distance < distances.get(adjacent)) {
distances.put(adjacent, distance);
priorityQueue.add(new Edge(adjacent, distance));
}
}
}
return distances;
}
}
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
Integer destination;
Integer distance;
public Edge(Integer destination, Integer distance) {
this.destination = destination;
this.distance = distance;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge edge) {
return this.distance - edge.distance;
}
}
# 신장트리
신장트리 (Spanning Tree)는 그래프의 모든 노드를 사이클 없이 연결한 트리다.
# 최소신장트리
- 가중치 그래프에서 모든 노드를 사이클 없이 최소 비용으로 연결하는 트리
- 최소신장트리를 찾는 방법에는 두 가지가 있다.
- 크루스컬 알고리즘
- 프림 알고리즘
# 크루스컬 알고리즘
- 모든 간선을 오름차순으로 연결한다.
- 최소 비용의 간선부터 선택한다.
- 사이클이 생기는 간선은 선택하지 않는다.
- 모든 노드가 연결될 때 까지 반복 실행한다.
public class Main {
static int[] parent;
static int V;
static int E;
static int cost = 0;
public static int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] == x) return x;
else return find(parent[x]);
}
public static void union(int x, int y) {
int xParent = find(x);
int yParent = find(y);
if (xParent > yParent) parent[x] = y;
else parent[y] = x;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
V = 6;
E = 9;
int[][] graph = {
{0, 1, 4}, // {정점 0, 정점 1, 가중치 4}
{0, 2, 3},
{1, 3, 5},
{1, 5, 9},
{2, 3, 2},
{2, 4, 6},
{3, 4, 1},
{3, 5, 8},
{4, 5, 15}
};
// 배열 parent 생성 & 초기화
parent = new int[6];
for (int i=0; i<parent.length; i++) parent[i] = i;
// graph를 가중치 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
Arrays.sort(graph, (int[] vertex1, int[] vertex2) -> vertex1[2] - vertex2[2]);
// MakeSet
for (int i=0; i<V; i++) parent[i] = i;
// 최소 가중치부터 크루스컬 알고리즘 진행
for (int i=0; i<E; i++) {
// 사이클이 존재하지 않는 경우에만 간선을 선택한다.
if (find(graph[i][0]) != find(graph[i][1])) {
cost += graph[i][2];
union(graph[i][0], graph[i][1]);
System.out.println("Selected Edge: " + Arrays.toString(graph[i]));
}
}
System.out.println("cost: " + cost);
}
}
// Selected Edge: [3, 4, 1]
// Selected Edge: [2, 3, 2]
// Selected Edge: [0, 2, 3]
// Selected Edge: [0, 1, 4]
// Selected Edge: [3, 5, 8]
// cost: 18
public class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
String nodeV;
String nodeU;
int weight;
public Edge(String nodeV, String nodeU, int weight) {
this.nodeV = nodeV;
this.nodeU = nodeU;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
"nodeV='" + nodeV + '\'' +
", nodeU='" + nodeU + '\'' +
", weight=" + weight +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge edge) {
return this.weight - edge.weight;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class KruskalPath {
HashMap<String, String> parent = new HashMap<String, String>();
HashMap<String, Integer> rank = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
public String find(String node) {
// 인자로 받은 노드의 루트 노드를 반환
if (parent.get(node) != node) {
parent.put(node, find(parent.get(node)));
}
return parent.get(node);
}
public void union(String nodeV, String nodeU) {
String root1 = find(nodeV);
String root2 = find(nodeU);
// 두 그래프를 union-by-rank 기법을 사용하여 연결
if (rank.get(root1) > rank.get(root2)) {
parent.put(root2, root1);
} else {
parent.put(root1, root2);
if (rank.get(root1) == rank.get(root2)) {
rank.put(root2, rank.get(root2) + 1);
}
}
}
// 초기화, 각 노드를 분리된 부분집합으로 만든다.
public void makeSet(String node) {
// 자신을 루트노드로 만듬.
parent.put(node, node);
rank.put(node, 0);
}
public ArrayList<Edge> kruskal(ArrayList<String> vertices, ArrayList<Edge> edges) {
ArrayList<Edge> MST = new ArrayList<Edge>();
Edge currentEdge;
// 초기화
for (int index=0; index<vertices.size(); index++) {
makeSet(vertices.get(index));
}
// 간선 weight로 sorting
Collections.sort(edges);
// weight가 작은 edge부터 뽑아서 하나씩 알고리즘 돌려본다.
for (int index=0; index<edges.size(); index++) {
currentEdge = edges.get(index);
// 싸이클이 없을 때만 합친다.
if (find(currentEdge.nodeV) != find(currentEdge.nodeU)) {
union(currentEdge.nodeV, currentEdge.nodeU);
MST.add(currentEdge);
}
}
return MST;
}
}
ArrayList<String> vertices = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G"));
ArrayList<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<Edge>();
edges.add(new Edge("A", "B", 7));
edges.add(new Edge("A", "D", 5));
edges.add(new Edge("B", "A", 7));
edges.add(new Edge("B", "D", 9));
edges.add(new Edge("B", "C", 8));
edges.add(new Edge("B", "E", 7));
edges.add(new Edge("C", "B", 8));
edges.add(new Edge("C", "E", 5));
edges.add(new Edge("D", "A", 5));
edges.add(new Edge("D", "B", 9));
edges.add(new Edge("D", "E", 7));
edges.add(new Edge("D", "F", 6));
edges.add(new Edge("E", "C", 5));
edges.add(new Edge("E", "D", 7));
edges.add(new Edge("E", "B", 7));
edges.add(new Edge("E", "F", 8));
edges.add(new Edge("E", "G", 9));
edges.add(new Edge("F", "D", 6));
edges.add(new Edge("F", "E", 8));
edges.add(new Edge("F", "G", 11));
edges.add(new Edge("G", "F", 11));
edges.add(new Edge("G", "E", 9));
KruskalPath kruskal = new KruskalPath();
ArrayList<Edge> result = kruskal.kruskal(vertices, edges);
System.out.println(result);
# 프림 알고리즘
- 시작 노드를 선택한다.
- 노드에 연결된 간선 중 가장 낮은 가중치를 선택한다.
- 선택된 노드에 연결된 간선도 포함하여 가장 낮은 가중치의 간선을 선택한다.
- 사이클이 생기는 간선은 선택하지 않는다.
public class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
public int weight;
public String node1;
public String node2;
public Edge(int weight, String node1, String node2) {
this.weight = weight;
this.node1 = node1;
this.node2 = node2;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
"weight=" + weight +
", node1='" + node1 + '\'' +
", node2='" + node2 + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge edge) {
return this.weight - edge.weight;
}
}
public class PrimPath {
public ArrayList<Edge> prim(String startNode, ArrayList<Edge> edges) {
Edge currentEdge, poppedEdge, adjacentEdgeNode;
ArrayList<Edge> currentEdgeList, candidateEdgeList, adjacentEdgeNodes;
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue;
ArrayList<String> connectedNodes = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<Edge> MST = new ArrayList<Edge>();
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Edge>> adjacentEdges = new HashMap<String, ArrayList<Edge>>();
for (int index=0; index<edges.size(); index++) {
currentEdge = edges.get(index);
if (!adjacentEdges.containsKey(currentEdge.node1)) {
adjacentEdges.put(currentEdge.node1, new ArrayList<Edge>());
}
if (!adjacentEdges.containsKey(currentEdge.node2)) {
adjacentEdges.put(currentEdge.node2, new ArrayList<Edge>());
}
for (int idx=0; index<edges.size(); idx++) {
currentEdge = edges.get(index);
currentEdgeList = adjacentEdges.get(currentEdge.node1);
currentEdgeList.add(new Edge(currentEdge.weight, currentEdge.node1, currentEdge.node2));
currentEdgeList = adjacentEdges.get(currentEdge.node2);
currentEdgeList.add(new Edge(currentEdge.weight, currentEdge.node2, currentEdge.node1));
}
connectedNodes.add(startNode);
candidateEdgeList = adjacentEdges.getOrDefault(startNode, new ArrayList<>());
priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<Edge>();
for (int idx=0; idx<candidateEdgeList.size(); idx++) {
priorityQueue.add(candidateEdgeList.get(index));
}
while(priorityQueue.size() > 0) {
poppedEdge = priorityQueue.poll();
if (!connectedNodes.contains(poppedEdge.node2)) {
// 해당 edge를 mst에 추가
connectedNodes.add(poppedEdge.node2);
MST.add(new Edge(poppedEdge.weight, poppedEdge.node1, poppedEdge.node2));
adjacentEdgeNodes = adjacentEdges.getOrDefault(poppedEdge.node2, new ArrayList<Edge>());
for (int idx=0; idx<adjacentEdgeNodes.size(); idx++) {
adjacentEdgeNode = adjacentEdgeNodes.get(idx);
if (!connectedNodes.contains(adjacentEdgeNode.node2)) {
priorityQueue.add(adjacentEdgeNode);
}
}
}
}
}
return MST;
}
}
ArrayList<String> vertices = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G"));
ArrayList<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<Edge>();
edges.add(new Edge(7, "A", "B"));
edges.add(new Edge(5, "A", "D"));
edges.add(new Edge(7, "B", "A"));
edges.add(new Edge(9, "B", "D"));
edges.add(new Edge(8, "B", "C"));
edges.add(new Edge(7, "B", "E"));
edges.add(new Edge(8, "C", "B"));
edges.add(new Edge(5, "C", "E"));
edges.add(new Edge(5, "D", "A"));
edges.add(new Edge(9, "D", "B"));
edges.add(new Edge(7, "D", "E"));
edges.add(new Edge(6, "D", "F"));
edges.add(new Edge(5, "E", "C"));
edges.add(new Edge(7, "E", "D"));
edges.add(new Edge(7, "E", "B"));
edges.add(new Edge(8, "E", "F"));
edges.add(new Edge(9 ,"E", "G"));
edges.add(new Edge(6, "F", "D"));
edges.add(new Edge(8, "F", "E"));
edges.add(new Edge(11, "F", "G"));
edges.add(new Edge(11, "G", "F"));
edges.add(new Edge(9, "G", "E"));
PrimPath prim = new PrimPath();
ArrayList<Edge> result = prim.prim("A", edges);
System.out.println(result);
← Introduction 알고리즘 →
