# Table of Contents
# 집합자료형(Collection)
Kotlin은 같은 타입의 데이터를 한꺼번에 쉽게 관리할 수 있도록 집합자료형(Collection)을 제공한다.
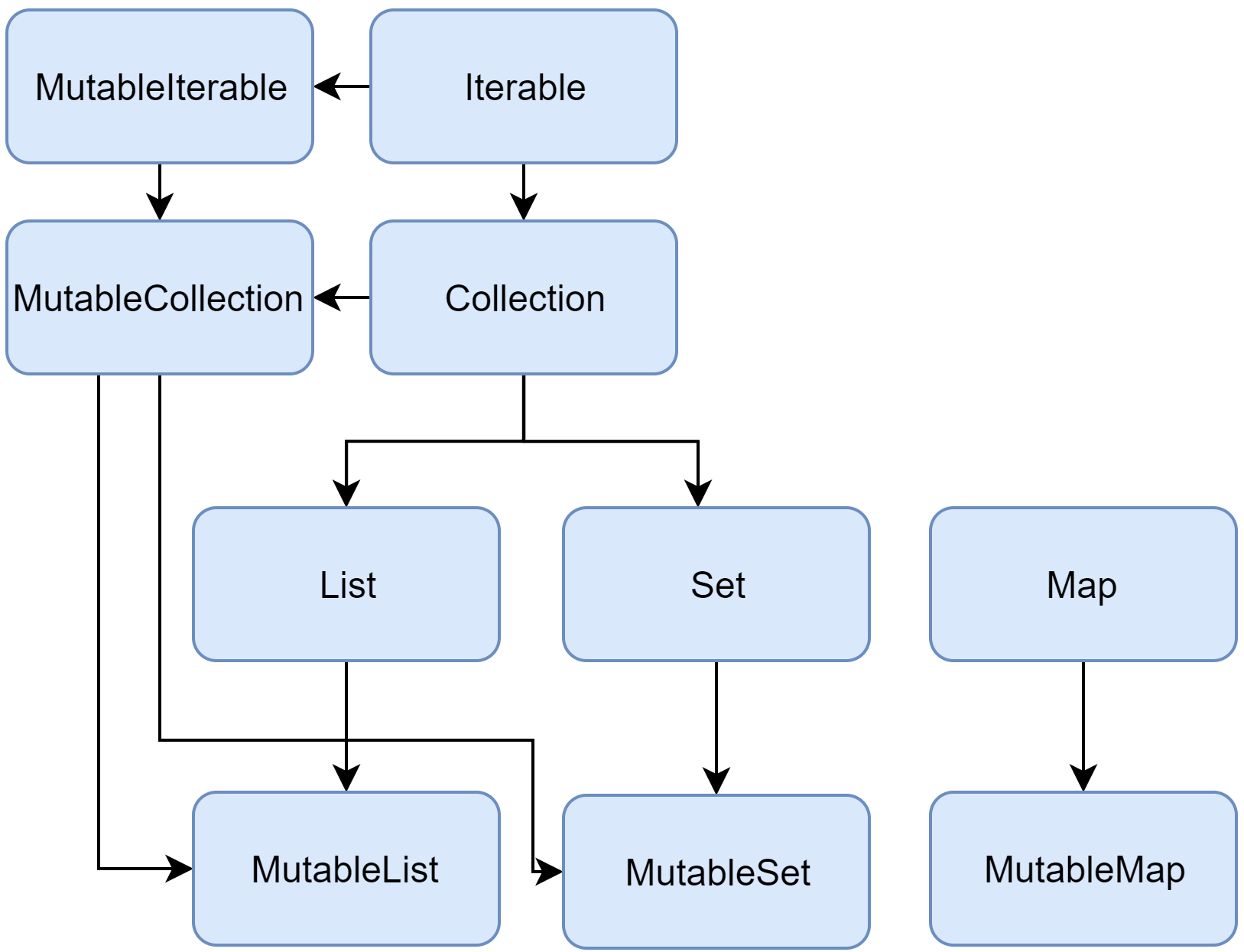
Kotlin이 제공하는 집합자료형은 Kotlin 표준 라이브러리에 포함되어있다.
# List
List는 다음 특징을 가진 집합 자료형이다.
- 순서가 있다.
- 중복을 허용한다.
# List
List는 생성 후 값을 추가, 삭제, 변경할 수 없다.
List는 listOf()메소드로 생성할 수 있다.
// 초기화 이후 추가, 삭제, 변경 불가능
val numbers: List<Int> = listOf(10, 20, 30)
// List의 요소에 접근만 가능
numbers.get(0)
List클래스의 생성자를 사용할 수도 있다.
val numbers: List<Int> = List<Int>(4, {index -> index})
for (number in numbers) {
println(number)
}
// 0
// 1
// 2
// 3
# MutableList
List는 생성 후 값을 추가, 삭제, 변경할 수 있다.
변경 가능한 리스트를 선언할 때는 mutableListOf()메소드를 사용한다.
// 데이터 추가, 삭제, 변경이 가능
val numbers: MutableList<Int> = mutableListOf(10, 20, 30)
// 리스트의 끝에 데이터 추가
numbers.add(40)
// 2번 인덱스에 데이터 추가
numbers.add(2, 15)
// 특정 요소 삭제
numbers.remove(15)
// 인덱스로 특정 요소 삭제
numbers.removeAt(20)
// 0번째 인덱스의 데이터 변경
numbers.set(0, 40)
// List의 크기
numbers.size
빈 리스트는 다음과 같이 생성한다.
val numbers: MutableList<Int> = mutableListOf()
MutableList클래스의 생성자를 사용할 수도 있다.
val numbers: MutableList<Int> = MutableList<Int>(5, {index -> index})
# List 순회
for in 구문으로 List를 순회할 수 있다.
for (number in numbers) {
println(number)
}
# Set
Set은 다음 특징을 갖는 자료구조다.
- 중복을 허용하지 않는다.
- 순서가 없다.
# setOf()
변경 불가능한 집합을 선언할 때는 setOf()메소드를 사용한다.
// 초기화 이후 추가, 삭제, 변경 불가능
var jobs: Set<String> = setOf("programmer", "designer", "footballer")
// 데이터 포함여부 확인
jobs.contains("programmer") // true
jobs.contains("singer") // false
# mutableSetOf()
변경 가능한 집합을 선언할 때는 mutableSetOf()메소드를 사용한다.
// 초기화 이후 추가, 삭제, 변경 가능
var jobs: MutableSet<String> = mutableSetOf("footballer", "programmer", "designer")
// 데이터 추가
jobs.add("CEO")
// 데이터 삭제
jobs.remove("footballer")
집합은 중복을 허락하지 않는다. 동일한 데이터를 여러 개 넣어도 한 개만 유지한다.
// 초기화 이후 추가, 삭제, 변경 가능
var jobs: MutableSet<String> = mutableSetOf()
jobs.add("footballer")
jobs.add("footballer")
jobs.add("footballer")
jobs.add("CEO")
println(jobs) // [footballer, CEO]
# Set 순회
for in 구문으로 Set을 순회할 수 있다.
var jobs: Set<String> = setOf("programmer", "designer", "footballer")
for (job in jobs) {
println(job)
}
# Map
Map은 키(Key)와 값(Value)으로 구성된 집합 자료형이다. 키를 통해 값을 저장하거나 읽어오거나 변경하거나 삭제할 수 있다.
# mapOf()
변경 불가능한 맵을 선언할 때는 mapOf()메소드를 사용한다.
var map: Map<String, String> = mapOf("name" to "paul", "job" to "programmer")
다음과 같이 키를 사용하여 값을 읽어올 수 있다.
map.get("job") // programmer
// map["job"]
# mutableMapOf()
변경 가능한 맵를 선언할 때는 mutableMapOf()메소드를 사용한다.
var mutableMap: MutableMap<String, String> = mutableMapOf("name" to "paul", "job" to "programmer")
다음과 같이 키를 사용하여 값을 변경할 수도 있다.
mutableMap.set("job", "designer")
// mutableMap["job"] = "designer"
키와 값을 추가할 수도 있다.
mutableMap.put("address", "Seoul")
// mutableMap["address"] = "Seoul"
Map의 toMutableMap()을 사용할 수도 있다.
var map: Map<Int, String> = mapOf(9 to "Benzema", 7 to "Ronaldo", 4 to "Ramos", 11 to "Bale")
var mutableMap = map.toMutableMap()
# sortedMapOf()
키(Key)로 맵을 정렬할 때는 sortedMapOf()를 사용한다.
var sortedMap: SortedMap<Int, String> = sortedMapOf()
sortedMap.put(11, "Bale")
sortedMap.put(4, "Ramos")
sortedMap.put(7, "Ronaldo")
sortedMap.put(9, "Benzema")
println(sortedMap) // {4=Ramos, 7=Ronaldo, 9=Benzema, 11=Bale}
첫 번째 인자로 Comparator를 전달할 수 있다.
var sortedMap: SortedMap<Int, String> = sortedMapOf({e1, e2 -> e2 - e1}, 9 to "Benzema", 7 to "Ronaldo", 4 to "Ramos", 11 to "Bale")
println(sortedMap) // {4=Ramos, 7=Ronaldo, 9=Benzema, 11=Bale}
MutableMap의 toSortedMap()메소드로 MutableMap을 SortedMap으로 변환할 수 있다.
var mutableMap: MutableMap<Int, String> = mutableMapOf(9 to "Benzema", 7 to "Ronaldo", 4 to "Ramos", 11 to "Bale")
var sortedMap = mutableMap.toSortedMap { e1, e2 -> e2 - e1 }
# linkedMapOf()
linkedMapOf()을 사용하면 데이터 삽입 순서를 보장할 수 있다.
val linkedMap: LinkedHashMap<Int, String> = linkedMapOf<Int, String>()
linkedMap.put(11, "Bale")
linkedMap.put(4, "Ramos")
linkedMap.put(7, "Ronaldo")
linkedMap.put(9, "Benzema")
println(linkedMap) // {11=Bale, 4=Ramos, 7=Ronaldo, 9=Benzema}
# Map 순회
Map인터페이스의 keys 속성으로 키 집합에 접근할 수 있다.
var map: Map<Int, String> = mapOf(9 to "Benzema", 7 to "Ronaldo", 4 to "Ramos", 11 to "Bale")
for (key in map.keys) {
println(map[key])
}
// Benzema
// Ronaldo
// Ramos
// Bale
Map인터페이스의 entries 속성으로 Map.Entry 집합에 접근할 수 있다.
var map: Map<Int, String> = mapOf(9 to "Benzema", 7 to "Ronaldo", 4 to "Ramos", 11 to "Bale")
for (entry in map.entries) {
println("${entry.key} : ${entry.value}")
}
// 9 : Benzema
// 7 : Ronaldo
// 4 : Ramos
// 11 : Bale
# Kotlin과 Java 표준 라이브러리
Kotlin에서는 Java 표준 라이브러리도 자유롭게 사용할 수 있다. 다만 java 표준 라이브러리를 임포트해야 한다.
import java.util.*
val numbers = ArrayList<Int>();
numbers.add(3)
numbers.add(1)
numbers.add(9)
numbers.add(7)
Collections.sort(numbers, Collections.reverseOrder())
# Stack
스택은 Java 표준 라이브러리의 Stack클래스를 사용한다.
import java.util.*
val stack = Stack<Int>()
stack.push(1)
stack.peek()
stack.pop()
# Queue
큐 역시 Java 표준 라이브러리의 Queue인터페이스와 LinkedList클래스를 사용한다.
import java.util.*
val queue: Queue<Int> = LinkedList<Int>()
queue.add(1)
queue.add(2)
queue.peek()
queue.remove()
# PriorityQueue
val heap: PriorityQueue<Int> = PriorityQueue(Collections.reverseOrder())
heap.add(1)
heap.add(2)
heap.add(3)
heap.peek()
val result: Int = heap.remove()
다음과 같이 Comparator를 사용할 수도 있다.
val heap: PriorityQueue<Int> = PriorityQueue { e1, e2 -> e1 - e2 }
